redo Jump to...
print Print...
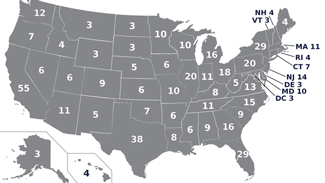
The U.S. Electoral College is made up of 538 members, representing all 50 states and the District of Columbia. States gain and lose electors based on Census data.
(from London’s Daily Telegraph) – 314 million Americans, 50 states, two candidates and well over a billion dollars in campaign spending. How does the U.S. election work?
The campaign comes down to one number: 270. That’s the number of electoral college votes [a candidate] needs to win and to claim the White House. The electoral college was created in the earliest days of the U.S. as a voting system that allows the disparate states to come together and elect a single president to represent them all.
Each state, plus Washington DC, is awarded a certain number of electoral votes based roughly on size. California, America’s largest state [in population], gets 55 votes while sparsely-populated Wyoming gets only three. All but two states use a winner-takes-all system, so if you win the most votes in a state you take its entire haul of electoral college votes. There are 538 electoral college votes in total and the candidate to get a majority – 270 – becomes president.
Strategists for Mitt Romney and Barack Obama have spent months and millions of dollars trying to figure out which combinations of states they need to win to get them over that crucial threshold of 270.
So how do they go about reaching 270?
By targeting “swing states” – a small group of about a dozen states that sometimes vote Democrat and sometimes vote Republican. [President Obama won all of the swing states in 2008.]
The vast majority of America’s states are considered solidly committed to one party – for example California is unfailingly Democrat while Texas always goes Republican. But others, like Florida, Ohio and Iowa, are open to persuasion. The campaigns focused their time, their money and their resources on winning these swing states and voters there were bombarded with advertising and endless visits from the candidates.
What happens on Election Day itself?
On the morning of November 6, polling booths will open in all 50 states and in Washington DC and around 100 million votes are expected to be cast. Counting begins immediately and when voting finishes in the evening we will get our first glimpse of the exit polls, surveys carried out throughout the day that give an idea of who won.
Usually by around 11pm on the East Coast it’s become clear that one side has prevailed. In that case the losing candidate calls the winner to concede. Both men will give a speech: one to claim victory and the other admit defeat.
But there is always the possibility – as happened in 2000 – that at the end of Election Day we may still not know who’s won. The result could either be too close to call without counting every vote or else legal battles over election procedures may delay the result or force a recount. It could even be a tie, with both candidates stuck at 269, in which case the House of Representatives would vote choose the next president. [Thomas Jefferson (in 1801) and John Quincy Adams (in 1825) were chosen by the House of Representatives because no candidate won a majority of the electoral votes. In Thomas Jefferson’s case it was because he and his opponent technically had the same number of votes. A Constitutional Amendment following the election prevented that from happening again. For John Quincy Adams, it was a four man race. Andrew Jackson won the most electoral votes, but was short of a majority.]
If Mitt Romney wins does he become president straight away?
No. The next president will be publicly sworn into office on January 21, 2013, in an inauguration ceremony at the U.S. Capitol in Washington DC. If Romney wins he’ll spend the time between November and January – known as “the transition” – assembling his cabinet, his White House staff and preparing for government. If Obama wins his administration will largely stay in place, although he may decide to reshuffle his cabinet and aides for his second term.
Are voters just casting ballots for the presidential election?
No. As well as voting for president, Americans are also electing all 435 members of Congress’s lower house, the House of Representatives, and one-third of the Senate. Plus, they are voting for a medley of local and state officials.
Information appearing on telegraph.co.uk is the copyright of Telegraph Media Group Limited and must not be reproduced in any medium without license. Reprinted here for educational purposes only. May not be reproduced on other websites without permission from the Telegraph. Visit the website at telegraph. co. uk.
Questions
NOTE TO STUDENTS: Before answering the questions, read the information under “Background” below and watch the video under “Resources.”
1. How many electoral college votes are there in total? On what numbers are they based?
2. How many electoral votes does a candidate need to win the presidency?
3. What are “swing states” (also known as “battleground” or “toss-up” states)?
4. What is the “transition”?
5. How many members of the House of Representatives were also elected this election day?
CHALLENGE QUESTION:
a) List the battleground states in the 2012 presidential election.
b) List the winner of each state’s electoral votes, and the number of popular votes each candidate received.
c) List the names and parties of the Representatives and (if applicable) Senators who won in your state. Who is the Representative for your district?
Background
THE ELECTORAL COLLEGE:
- The Electoral College was established by the U.S. Constitution (Article II, Section I). The Wall Street Journal says: “This Electoral College was built into the U.S. Constitution because the country’s founders were skeptical about having elections determined by direct popular will and also wanted to ensure small states had a voice in national affairs.”
- The Electoral College is the institution that officially elects the President and Vice President of the United States every four years.
- The total of U.S. electoral votes is 538. A candidate needs 270 electoral votes to win the presidency – it’s half of 538, plus one.
- The number 538 is the sum of the nation’s 435 Representatives, 100 Senators, and 3 electors given to the District of Columbia. (i.e. Each state gets one elector per member of Congress.) e.g. Alaska gets three electoral votes, because there are two senators and one representative in Congress from that state. California gets 55 electoral votes, because there are two senators and 53 representatives in Congress from that state.
- A candidate who wins the majority of votes in a state gets all its electoral votes. The exceptions to this rule are Nebraska and Maine, where the state winner gets the two electoral votes derived from the two senators, while the candidate who wins each congressional district gets the electoral vote derived from that representative.
- Technically, the election of the president of the United States takes place during a joint session of Congress on January 6th following Election Day. That’s when members of the House and Senate meet in the House chamber to preside over the counting of electors’ votes.
How many Presidential candidates lost the popular vote but won the election by winning the electoral college vote?
- John Quincy Adams 1824 (elected by Congress) over Andrew Jackson
- Rutherford B Hayes 1876 (declared the Electoral College winner by an Electoral Commission) over Samuel J Tilden
- Benjamin Harrison 1888 won over Grover Cleveland
- George W. Bush 2000 (After disputed Florida electors were awarded to him by Supreme Court Ruling) over Al Gore. The last recount showed that Bush won.
(NOTE: Samuel Tilden actually won more than half of the popular vote. The others only won a plurality [more votes than the other candidate, but not a more than half the votes].)
from wikianswers.com
SWING STATES:
A swing state, also referred to as a battleground state (or purple state because it is not majority Democratic “Blue State” or Republican “Red State”) is a state in which no single candidate or party has overwhelming support in securing that state’s electoral college votes. Such states are targets of both major political parties in presidential elections, since winning these states is the best opportunity for a party to gain electoral votes. Non-swing states are sometimes called safe states, because one candidate has strong enough support that he or she can safely assume that he or she will win the state’s votes. (from wikipedia) [Watch an explanation in the video under “Resources” below.]
Daily “Answers” emails are provided for Daily News Articles, Tuesday’s World Events and Friday’s News Quiz.



