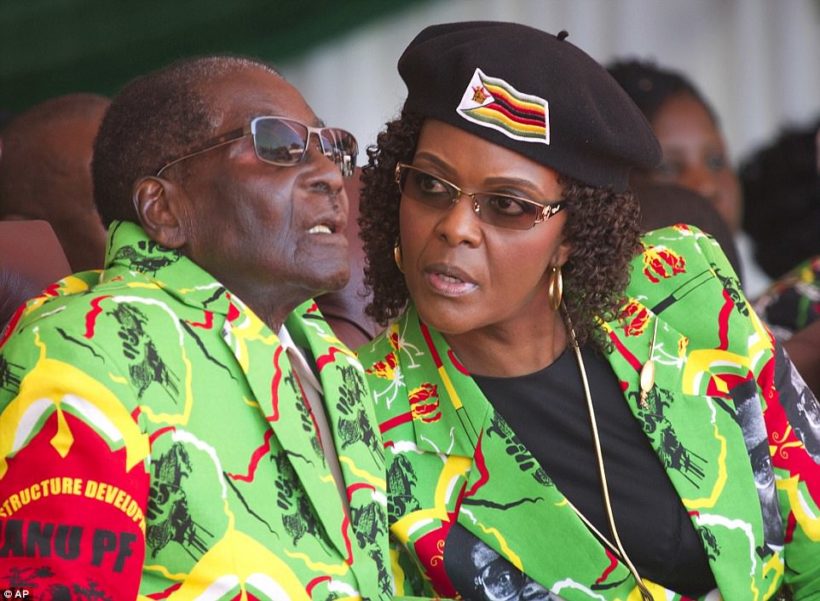
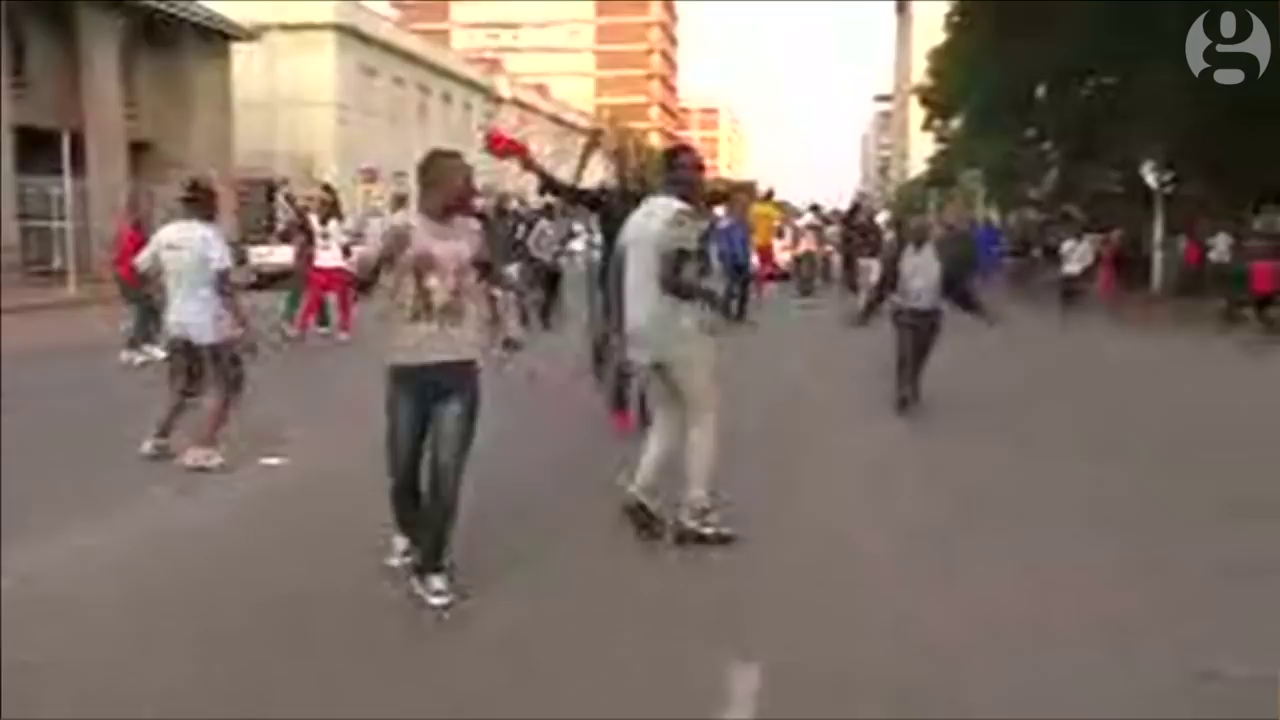Robert Mugabe, 93, could leave Zimbabwe after resigning as president after 37 years, but the military is demanding that reviled second wife Grace, 52 (pictured together), is left behind to face prosecution.
redo Jump to...
print Print...
(by MacDonald Dzirutwe, Reuters, Nov. 21) HARARE – Robert Mugabe resigned as Zimbabwe’s president on Tuesday (Nov. 21), a week after the army and his former political allies moved to end four decades of rule by a man once feted as an independence hero who became feared as a despot.
His former vice president, Emmerson Mnangagwa, whose firing this month prompted the military takeover that forced Mugabe out, [was] sworn in as president on [Friday, Nov. 24], Patrick Chinamasa, legal secretary of the ruling ZANU-PF party, told Reuters.
The 93-year-old Mugabe had clung on for a week after an army takeover, with his party ZANU-PF urging him to go. He finally resigned moments after parliament began an impeachment process seen as the only legal way to force him out.
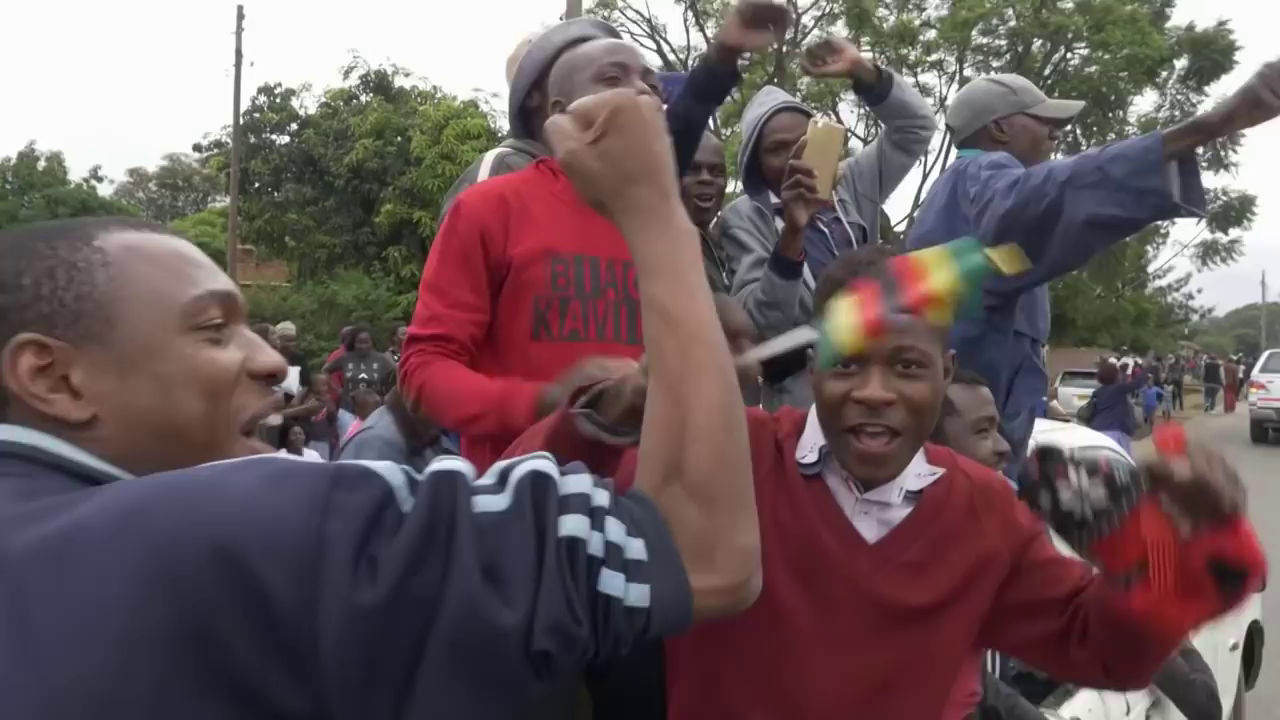
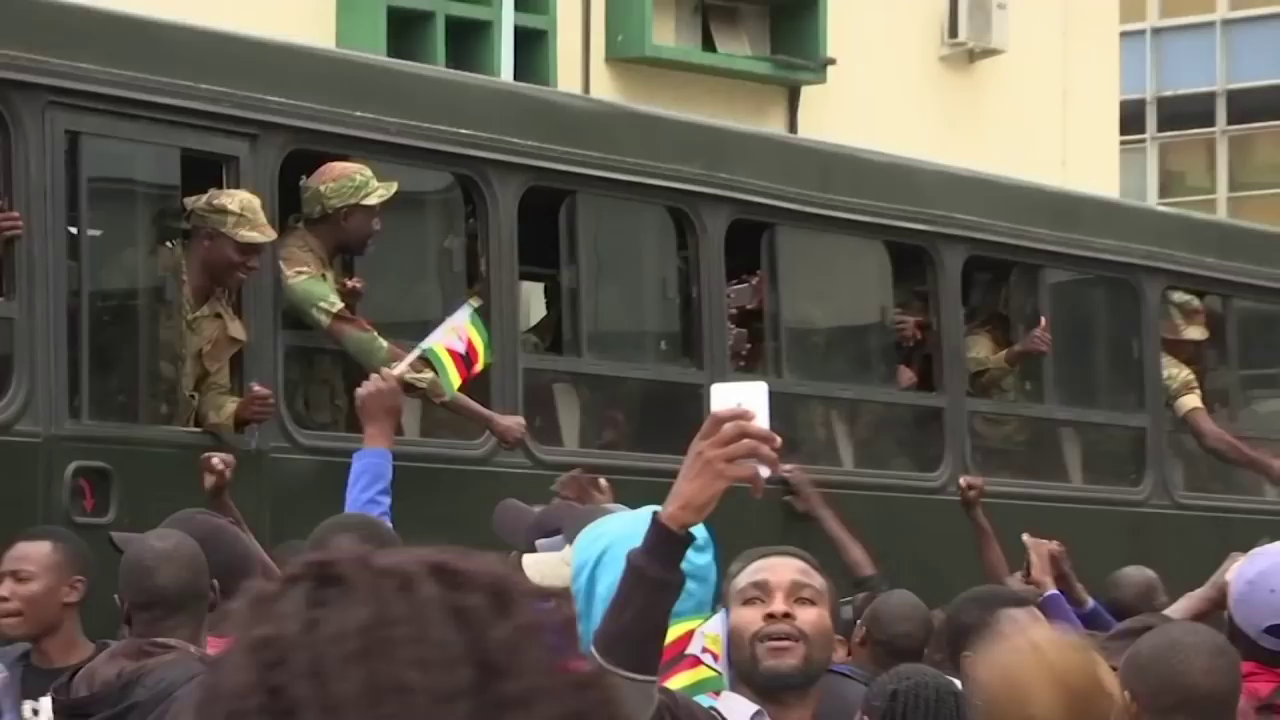
Wild celebrations broke out at a joint sitting of parliament when Speaker Jacob Mudenda read out Mugabe’s brief resignation letter. Mugabe, confined to his Harare residence, did not appear.
People danced in the streets of Harare and car horns blared at the news that the era of Mugabe — who had led Zimbabwe since independence in 1980 — was finally over. Some brandished posters of Mnangagwa and army chief General Constantino Chiwenga.
The army seized power after Mugabe sacked Mnangagwa, ZANU-PF’s favorite to succeed him, in a bid to smooth a path to the presidency for his wife Grace, 52, known to her critics as “Gucci Grace” for her reputed fondness for luxury shopping.
…Thousands of people rallied against Mugabe in the days after the army intervened. Since the crisis began, Mugabe has been mainly confined to his “Blue Roof” mansion in the capital where Grace is also believed to be.
ZANU-PF chief whip Lovemore Matuke told Reuters that Mnangagwa would be sworn in within 48 hours and serve the remainder of Mugabe’s term until the next election, which must be held by September 2018.
“I am very happy with what has happened,” said Maria Sabawu, a supporter of the opposition Movement for Democratic Change (MDC), outside the hotel where the impeachment process was happening.
“I have suffered a lot at the hands of Mugabe’s government,” she said, showing her hand with a missing finger that she said was lost in violence during a presidential run-off election between Mugabe and opposition leader Morgan Tsvangirai in 2008.
Mugabe had led Zimbabwe since a guerrilla struggle ended white-minority rule in the British colony formerly known as Rhodesia.
He took the once-rich nation to economic ruin, leading the forced takeover of white-owned farms at the end of the century (by 2000), which devastated agricultural foreign exchange earnings and led to hyperinflation.
(He was able to stay popular by) brandishing his anti-colonial credentials and styling himself the Grand Old Man of African politics and he retained the admiration of many people across the continent.
Amnesty International, however, said that under Mugabe tens of thousands of people were tortured, forcibly disappeared or killed in a culture of impunity that allowed “grotesque crimes to thrive.”
“The people of Zimbabwe deserve better. The next generation of leaders must commit itself to upholding the constitution, living up to Zimbabwe’s international human rights obligations and treating its people with dignity and justice,” the rights group said in a statement.
Questions
1. For ZIMBABWE, give the following information:
- capital
- location/the countries that share its borders
- the religious breakdown of the population
- the type of government
- the chief of state (and head of government if different) If monarch or dictator, since what date has he/she ruled? – include name of heir apparent for monarch
- the population
Find the answers at the CIA World FactBook website. For each country, answers can be found under the “Geography” “People” and “Government” headings.
NOTE: Before answering the questions below, read the info under “Background” and watch the video under “Resources.”
2. For ZIMBABWE:
a) list the who, what, where and when of the news item
b) Why did the army force Mugabe out?
c) Why did Mugabe fire his vice president?
d) What caused Mugabe to finally resign?
e) What accusations did Amnesty International make against Mugabe?
f) What did Amnesty call on the new leaders of Zimbabwe to do?
Background
From the Reuters article above:
Mnangagwa, 75, who fled Zimbabwe after his sacking in fear for his safety, was a chief lieutenant to Mugabe for decades and himself stands accused of participating in repression.
He was internal security chief in the mid-1980s when Mugabe deployed a North Korean-trained brigade against rebels during which 20,000 civilians were killed, according to rights groups.
Reuters reported in September that Mnangagwa was plotting to succeed Mugabe, with army backing, at the helm of a broad coalition to seek Zimbabwe’s re-engagement with the world after decades of isolation from global lenders and donors.
Nicknamed “Ngwena”, or crocodile in the Shona language, an animal famed in Zimbabwean lore for its stealth and ruthlessness, Mnangagwa issued a statement from hiding on Tuesday calling on Zimbabweans to unite to rebuild the country.
Opposition politician and former education minister David Coltart said that call gave hope of lifting a shattered economy from its knees, provided Mnangagwa made good on his promise to reach out to other factions.
“When we all wake up with hangovers tomorrow, we will be reminded of the dreadful state our nation is in – no money in the banks and businesses collapsing,” Coltart told Reuters.
“As Emmerson Mnangagwa said, ZANU-PF is not capable of resolving this issue on its own. I took some comfort from his words. If he translates them into action, the future is positive.”
Mugabe’s ‘legacy’:
- The UK annexed Southern Rhodesia from the former British South Africa Company in 1923. A 1961 constitution was formulated that favored whites in power. In 1965 the government unilaterally declared its independence, but the UK did not recognize the act and demanded more complete voting rights for the black African majority in the country (then called Rhodesia).
- UN sanctions and a guerrilla uprising finally led to free elections in 1979 and independence (as Zimbabwe) in 1980.
- Robert Mugabe, the nation’s first prime minister, has been the country’s only ruler (as president since 1987) and has dominated the country’s political system since independence.
- His chaotic land redistribution campaign (in which the government confiscated farms owned by whites and gave them to blacks), which began in 1997 and intensified after 2000, caused an exodus of white farmers, crippled the economy, and ushered in widespread shortages of basic commodities.
- Ignoring international condemnation, Mugabe rigged the 2002 presidential election to ensure his reelection.
- In 2005, the capital city of Harare embarked on Operation Restore Order, ostensibly an urban rationalization program, but was really a government-led destruction of the homes or businesses of 700,000 mostly poor supporters of the opposition political party.
- Mugabe in 2007 instituted price controls on all basic commodities causing panic buying and leaving store shelves empty for months.
- General elections held in March 2008 contained irregularities but still amounted to a censure of the ZANU-PF-led government with the opposition winning a majority of seats in parliament. Movement for Democratic Change – Tsvangirai opposition leader Morgan Tsvangirai won the most votes in the presidential poll, but not enough to win outright.
- In the lead up to a run-off election in June 2008, considerable violence against opposition party members led to the withdrawal of Tsvangirai from the ballot. Extensive evidence of violence and intimidation resulted in international condemnation of the process.
- Difficult negotiations over a power-sharing “government of national unity,” in which Mugabe remained president and Tsvangirai became prime minister, were finally settled in February 2009, although the leaders failed to agree upon many key outstanding governmental issues.
- Mugabe was reelected president in 2013 in balloting that was severely flawed and internationally condemned. As a prerequisite to holding the election, Zimbabwe enacted a new constitution by referendum, although many provisions in the new constitution have yet to be codified in law.
Resources
Watch a Nov. 18 Channel 4 News report:
Watch a Nov. 18 AP report:
Watch a Nov. 21 Guardian News report:
Daily “Answers” emails are provided for Daily News Articles, Tuesday’s World Events and Friday’s News Quiz.