redo Jump to...
print Print...

President Obama speaks at a National Action Network conference Friday, April 11, 2014, in New York. (AP/The Daily News, Julia Xanthos, Pool)
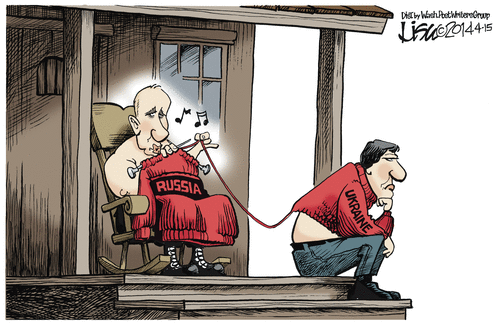
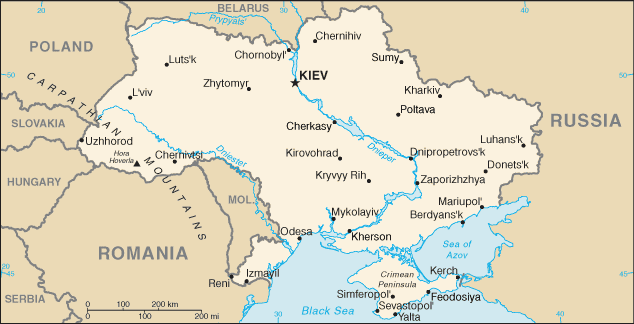
(by Julie Pace, Associated Press) WASHINGTON – With the White House asserting that Russia is stoking instability in eastern Ukraine, President Barack Obama is once again faced with the complicated reality of following through on his tough warnings against overseas provocations.
The President has vowed repeatedly to enact biting sanctions against Russia’s vital economic sectors if the Kremlin tries to replicate its actions in Crimea, the peninsula it annexed [took over] from Ukraine, elsewhere in the former Soviet republic. Despite those warnings, Russian President Vladimir Putin appears to be testing Obama’s limits, instigating protests in eastern Ukraine, the White House says, and massing tens of thousands of troops on the border, but so far stopping short of a full-scale military incursion. …
For President Obama, the U.S. response to the chaos in Ukraine has become more than a test of his ability to stop Russia’s advances. It’s also being viewed through the prism of his decision last summer to back away from his threat to launch a military strike when Syria crossed his chemical weapons “red line” – a decision that has fed into a narrative pushed by Obama’s critics that the president talks tough, but doesn’t follow through.
While there has been no talk of “red lines” when dealing with Putin, Obama has said repeatedly that the Kremlin’s advances into eastern Ukraine would be a “serious escalation” of the conflict that would warrant broad international sanctions on the Russian economy. But perhaps trying to avoid another Syria scenario, White House officials have carefully avoided defining what exactly would meet Obama’s definition of a “serious escalation,” even as they make clear that they believe Russia is fomenting [instigating] the violence in cities throughout Ukraine’s vital industrial east.
“We are actively evaluating what is happening in eastern Ukraine, what actions Russia has taken, what transgressions they’ve engaged in,” White House spokesman Jay Carney said Monday. “And we are working with our partners and assessing for ourselves what response we may choose.”
As with the situation in Syria, Obama faces few good options as he watches Russia destabilize Ukraine, the former Soviet republic that has sought greater ties with Europe.
 There’s little appetite in either the U.S. or Europe for direct military action, and the White House said Monday it was not actively considering sending Ukraine lethal assistance. That’s left Obama and his international partners largely reliant on economic and diplomatic retaliation.
There’s little appetite in either the U.S. or Europe for direct military action, and the White House said Monday it was not actively considering sending Ukraine lethal assistance. That’s left Obama and his international partners largely reliant on economic and diplomatic retaliation.
The president has wielded some of his available options since the situation in Ukraine devolved in late February, but those actions so far have had little success in stopping Russian advances.
Obama’s initial warning that Putin would face “costs” if he pressed into Crimea was largely brushed aside by the Russian leader, who went so far as to formally annex [take control of] the peninsula from Ukraine. Economic sanctions on several of Putin’s closest associates followed, as did Russia’s suspension from the exclusive Group of Eight economic forum, but neither appears to have discouraged Moscow from making a play for eastern Ukraine.
On Friday, the U.S. slapped sanctions on more individuals connected to the Crimea takeover, and White House officials are weighing another round of targeted penalties against additional Russian and Ukrainian citizens.
But with tens of thousands of troops massed on Russia’s border with eastern Ukraine, Obama is facing calls from some Republicans to take tougher action now. Tennessee Sen. Bob Corker, the top Republican on the Senate Foreign Relations Committee, sent Obama a letter over the weekend calling on the administration to immediately ratchet up economic penalties against Moscow.
“Rather than wait for a Russian invasion of eastern Ukraine to implement additional sanctions, which seems to be U.S. policy at the moment, we must take action now that will prevent this worst-case scenario before it becomes a reality,” Corker wrote.
Privately, some of Obama’s advisers are also pushing for more robust penalties now to serve as a deterrent against a full-on Russian military incursion. But questions remain about Europe’s commitment to take the kind of coordinated action that would stand the best chance of changing Putin’s calculus.
Europe has a far deeper economic relationship with Russia than the U.S., meaning its sanctions would hurt Moscow more. But leaders on the still economically shaky continent fear that the impact of those sanctions could boomerang and hurt their own countries just as much.
European foreign ministers met Monday to debate whether additional sanctions should be enacted on Russia. A high-ranking European Union official said they did decide to sanction more Russians with asset freezes and visa bans, but they appeared to stop well short of targeting Russia’s broader economy.
Reprinted here for educational purposes only. May not be reproduced on other websites without permission from the Associated Press. Visit the website at ap .com.
Questions
1. What has President Obama repeatedly threatened to do if Russia tries to annex (take control of) any other part of Ukraine the way it did with Crimea last month?
2. What has President Obama said repeatedly about Russia’s possible advances into eastern Ukraine?
3. What part does the Obama administration think Russia is playing in the latest unrest in eastern Ukraine?
4. How are President Obama and his administration responding to the instability in Ukraine?
5. How effective have President Obama’s policies been thus far in addressing the crisis in Ukraine?
6. How did Russia’s President Vladimir Putin respond to President Obama’s initial warning?
7. a) What action is Republican Senator Bob Corker calling on President Obama to make?
b) Do you agree with Sen. Corker? Why or why not?
8. Who else is calling on President Obama to enact more sanctions against Russia now, not later?
9. On March 24, Agence France-Press news service reported:“US President Barack Obama on Monday vowed Western unity in punishing Moscow for annexing Crimea, ahead of crisis talks that could see Russia excluded from the G8 club of rich nations.
Obama told journalists at Amsterdam’s Rijksmuseum, “Europe and America are united in our support of the Ukrainian government and the Ukrainian people, we’re united in imposing a cost on Russia for its actions so far.”
What did European leaders agree to do on Monday regarding Russia’s involvement in Ukraine?
Daily “Answers” emails are provided for Daily News Articles, Tuesday’s World Events and Friday’s News Quiz.