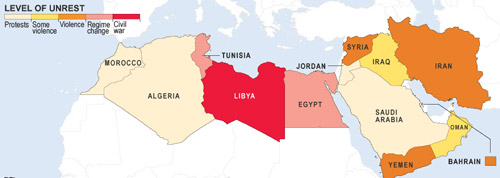
Syrian Army Uses Tanks against the People
Daily News Article — Posted on April 27, 2011
Note: This article is from the British newspaper The Daily Telegraph.
(by Adrian Blomfield, Middle East Correspondent and Jon Swaine in New York, Telegraph.co.uk) – Dozens of people were reportedly killed after [Syrian President Bashar Assad’s] troops and armor flooded into the southern city of Dera’a and opened fire on residential areas, apparently at random.
Amid growing international condemnation at the mounting death toll in Syria, where more than 100 protesters were killed on Good Friday alone, members of the UN Security Council are considering a statement being circulated by a British-led group of European countries, which condemned the killing of hundreds of Syrian protesters.
The statement, which was proposed with France, Germany and Portugal, called [on the Syrian government] for an immediate restraint, an end to the state of emergency, and an independent investigation into the civilian deaths. It could be released on Tuesday if approved by China and Russia, a western diplomat at the UN said.
The diplomat said the measure was aimed at “putting Syria on notice” that the Security Council was closely monitoring developments. “There may be talk of sanctions,” the diplomat said. “At present the focus is on releasing as strong a statement as is possible and securing the reforms that Syria has promised”.
The diplomat’s comments came as the United States threatened to impose sanctions on Mr. Assad and his henchmen in a significant policy shift.
“The brutal violence used by the government of Syria against its own people is completely deplorable,” said Tommy Vietor, a spokesman for the [U.S.] National Security Council.
The Obama administration has been criticized for its perceived reluctance to criticize Mr. Assad, a U.S. foe who is nonetheless seen as a bulwark against instability on the Syria-Israeli border, even as Nato [North Atlantic Treaty Organization (an alliance of 28 countries)] has bombed Libya.
But U.S. sanctions alone are unlikely to have much impact on Mr. Assad, who has abandoned all pretence of restraint in recent days.
When the tanks rolled into Dera’a, where the uprising against the government first began, there were no protesters on its streets. It was 4:30 a.m. and most people were still asleep, though some were walking towards mosques for dawn prayers.
From loudspeakers in places of worship across the city, imams broadcast frantic messages warning people to take cover – but it was too late. Without warning, the firing began.
“They entered the city from each of its four corners and just started shooting,” a resident of Dera’a said. “They are breaking into people’s homes and opening fire into their houses.”
Witnesses estimated that up to 5,000 troops, supported by armoured personnel carriers and at least seven tanks, advanced on the city.
Amateur video footage smuggled out of Dera’a showed soldiers erecting mounted machine guns before opening fire. The nearby border with Jordan, from where the explosion of artillery shells was clearly audible, was sealed off to prevent escape.
The wounded were dragged into nearby houses, which were turned into makeshift hospitals, blood dripping onto living room floors. Some activists said that 25 people had been killed, but others said there was no way of verifying the death toll.
“There is no way of knowing how many casualties there are because they are still lying out on the streets and you can’t use ambulances because the security forces are hiding inside them,” said Ausama Monajed, a Syrian political activist in touch with people in Dera’a.
Security forces also staged similar raids in Douma, on the outskirts of Damascus, while at least 13 civilians were said to have been killed since a military operation began in the coastal town of Jabla.
Video footage from Jabla showed gunfire being directed at unarmed protesters marching down a street. As the shots rang out, the demonstrators sat down on the road, only to come under fire again. One man, shot in the back of the head, was seen being carried back by fellow protesters as the gunfire continued.
A second clip showed another man dying from a gunshot wound in his neck.
The change in tactics appeared designed to keep protesters from gathering on the streets, a strategy that smacked of desperation, Mr. Monajed said.
“They have made up their mind, they are going to use the army now because they know the end is close,” he said. “The more emphasis we put on non-violence and the more brutal they become, the shorter this will be because there will be more defections from around the regime.”
There were unverified reports that some soldiers and junior officers involved in the operations in Dera’a had joined the protesters.
But observers said the large-scale military defections seen in Libya and Egypt were unlikely to be repeated in Syria, where the vast majority of senior officers come from Mr. Assad’s Allawite Shia sect, a minority that stands to lose its privileges if the Sunni majority comes to power as a result of the uprising.
Information appearing on telegraph.co.uk is the copyright of Telegraph Media Group Limited and must not be reproduced in any medium without licence. Reprinted here for educational purposes only. May not be reproduced on other websites without permission from the Telegraph. Visit the website at telegraph.co.uk.
Background
ON U.S.-SYRIAN RELATIONS:
- Bashar Assad became president on his father's death in 2000. Despite his pledges to liberalize [the government] he continues to restrict civil liberties and hold onto power by force, and human rights groups name Syria among the world's 20 most repressive countries today, citing thousands of political prisoners, restrictions on freedom of expression and association, and a state of emergency in place since 1963.
- Assad, like his father, has nurtured strong ties with Iran and the Lebanese terrorist group Hezbollah, while continuing to host Palestinian terrorist groups in Damascus.
- He also maintained Syria's decades-old policy of political and military interference in Lebanon, and his regime was suspected of high-level involvement in the assassination of former Lebanese Prime Minister Rafik Hariri in 2005. (from cnsnews.com)
- Syria has been on the U.S. list of state sponsors of terrorism since the list's inception in 1979.
- Because of its continuing support and safe haven for terrorist organizations, Syria is subject to legislatively mandated penalties, including export sanctions and ineligibility to receive most forms of U.S. aid or to purchase U.S. military equipment.
- In 1986, the U.S. withdrew its ambassador and imposed additional administrative sanctions on Syria in response to evidence of direct Syrian involvement in an attempt to blow up an Israeli airplane.
- A U.S. ambassador returned to Damascus in 1987, partially in response to positive Syrian actions against terrorism such as expelling the Abu Nidal Organization from Syria and helping free an American hostage earlier that year.
- However, relations since the February 2005 assassination of former Lebanese Prime Minister Hariri have considerably deteriorated.
- Issues of U.S. concern include the Syrian government's failure to prevent Syria from becoming a major transit point for foreign fighters entering Iraq, its refusal to deport from Syria former Saddam regime elements who are supporting the insurgency in Iraq, its ongoing interference in Lebanese affairs, its protection of the leadership of Palestinian rejectionist groups in Damascus, its deplorable human rights record, and its pursuit of weapons of mass destruction.
- In May 2004, the Bush administration, pursuant to the provisions of the Syrian Accountability and Lebanese Sovereignty Restoration Act, imposed sanctions on Syria which banned nearly all exports to Syria except food and medicine.
- In February 2005, in the wake of the Hariri assassination, the U.S. recalled its Ambassador to Washington.
- Since 2009, the Obama administration has attempted to engage with Syria to find areas of mutual interest, reduce regional tensions, and promote Middle East peace. These efforts have included congressional and executive meetings with senior Syrian officials, including President Asad, and the return of a U.S. Ambassador to Damascus. (from the U.S. State Department's website at www.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/3580.htm)
