redo Jump to...
print Print...
Example of Media Bias:
(by Sam Dorman, MRC Business, Feb. 18, 2016):
A mosquito-borne “epidemic” of Zika virus has spread around the world from Brazil to at least 9 other countries, provoking concern from health officials and those most at risk for the illness. Millions of people could be exposed to Zika, according to the broadcast networks.
The virus itself causes fever, rashes, joint pain and red eyes, but scientists and doctors in Brazil fear it is connected to the “skyrocketing” number of cases of microcephaly (a birth defect)….
The network news have warned about the threat of Zika and efforts to eradicate the Aedes mosquitos carrying it, but have mostly ignored one proposed means of doing just that: the insecticide DDT which once helped control the mosquito population.
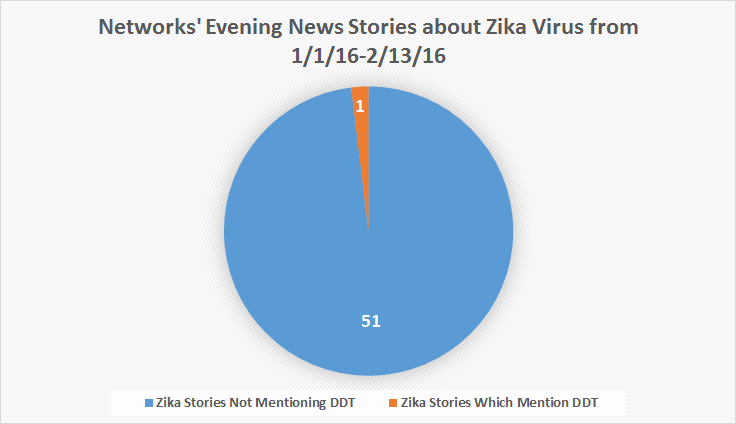
- In spite of past success with DDT and current proponents, 98 percent (51 out of 52) of stories about the Zika virus ABC, CBS and NBC evening news programming [did not] mention DDT — an insecticide which “drastically cut” the population of the mosquitos between the 1930s and 1970s.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) banned DDT in 1972 after environmentalists like Rachel Carson claimed it harmed the environment.
The admission of DDT’s effectiveness came from NBC Nightly News on Feb. 3 — the only network story to mention that insecticide by name between May 1, 2015 to Feb. 3, 2016. It also proved at least one of the broadcast networks was aware of the usefulness of DDT in eradicating mosquitoes and controlling diseases they spread.
Dr. Jane Orient, executive director of the Association of American Physicians and Surgeons, and some others have called for a return to DDT use in order to fight the Zika virus. The networks have ignored such proposals, while other media outlets like Time argued against its return by turning to health officials who viewed that as “potentially very misguided.”
The reason the Zika crisis has caused so much concern, is that a “cluster” of microcephaly (which causes children to be born with abnormally small heads) and a rare neurological disorder has been found in regions affected by Zika. Thousands have been affected. That prompted an emergency meeting of World Health Organization (WHO) on Feb. 1. WHO declared that the recent cases reported in Brazil were a “Public Health Emergency of International Concern” and urged further study to see if Zika virus was causing those disorders.
BBC reported that Brazilian scientists found the Zika “actively present” in the brains of two babies who died after only 48 hours. Health officials said more study is needed to determine the possible link between Zika virus and birth and neurological defects.
“Possible links with neurological complications and birth malformations have rapidly changed the risk profile for Zika from a mild threat to one of very serious proportions,” WHO director-general Margaret Chan said in the WHO Strategic Response Framework and Joint Operations Plan issued in Geneva, according to Reuters.
The virus, which is spread by a particular kind of mosquito, has already affected thousands of people in South America, and spread even to the United States. The Washington Post warned that Venezuelans may suffer even more due to poor medical care and the socialist government’s refusal to inform people about the disease.
The Colombian government said more than 5,000 pregnant women had the Zika virus, according to Reuters. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) said that Zika could be spread from pregnant women to their unborn children. …
Networks Ignore Voices Supporting DDT Use
In the wake of Zika’s spread, some doctors have called on authorities to combat the mosquitoes carrying the virus with DDT.
Like the EPA, the World Health Organization also opposed DDT use for years., But WHO reversed itself on indoor use of DDT in 2006, giving it a “clean bill of health for controlling malaria” and calling it “most effective.”
In the one network Zika story that mentioned DDT, NBC’s Nightly News reported that the mosquito population carrying Zika suffered devastating losses after the pesticide was used.
“These mosquitoes were widespread in the Americas during the 1930s. Aggressive control efforts, including the insecticide DDT, drastically cut their population by the ’70s, but now they are surging again,” NBC correspondent Rehema Ellis said.
However, every other evening news story about Zika ignored DDT as a potential weapon in the fight; even the stories that focused on mosquito eradication efforts. For example, CBS Evening News on Feb. 2, 2016, chief medical correspondent Dr. Jon Lapook reported on the Brazilian army and health workers killing mosquitos in neighborhoods.
“It’s a search and destroy mission by government workers. Each morning, teams of army and health workers target neighborhoods in the city of Recife, looking to kill mosquitoes that may carry the Zika virus,” said Lapook. He also interviewed a woman whose house was targeted by health officials.
“A worker added a chemical to kill mosquito larvae in a water storage tank at her house. The majority of breeding of this species of mosquito occurs in people’s homes,” Lapook said.
What Lapook did not bring up was the fact that the Brazilian government was not using DDT, although DDT has been effective at lowering mosquito populations and reducing the diseases they transmit. He didn’t even ask the question.
According to Dr. Gilbert Ross, Senior Director of Medicine and Public Health at the American Council on Science and Health, using DDT might halt the spread of Zika. In an op-ed published the same day as Lapook’s report, Ross advocated using DDT to fight the virus.
“Perhaps there is one legitimate solution: DDT. While it is not perfect (some resistance to the chemical may have emerged in the past), it may represent the best chance to hold this epidemic at least partly in check,” Ross wrote.
Ross also criticized the environmentalist movement for demonizing DDT and getting it banned, ultimately costing lives.
“The green movement decided, decades ago, that the lives of sub-Saharan African[s] did not matter as much as eggshell thinning, and millions subsequently died from malaria,” Ross wrote. “Now is the time for all to agree that the enviro-antipathy to DDT is baseless, and that if the impending Zika catastrophe is to be prevented in time, we need to use it.”
Dr. Jane Orient, executive director of the Association of American Physicians and Surgeons (AAPS), had a similar view. She told Breitbart News that DDT could help prevent the spread of Zika because “DDT was the most effective public health weapon of all time.”
Orient criticized the US ban on DDT as a poor decision by William Ruckelshaus, former head of the EPA.
“The ban on DDT was basically the decision of one man, William Ruckelshaus, going against a mountain of evidence on safety and enormous health benefits,” Orient said.
Orient explained, “It was said that, ‘If they can ban DDT, they can ban anything.’ And that’s how the EPA power grab started. Millions of African babies have died and are still dying of malaria because of [the ban on DDT].” …
(by Sam Dorman, MRC Business, Feb. 18, 2016) Methodology: MRC Business searched Nexis transcripts of evening news shows (Nightly News, Evening News, World News) about Zika between Jan. 1, 2016, to Feb. 13, 2016. Each of the transcripts were examined for mentions of the term DDT. MRC Business found 52 total stories or mentions of Zika, and only one of them mentioned DDT.
To accurately identify different types of bias, you should be aware of the issues of the day, and the liberal and conservative perspectives on each issue.
Types of Media Bias:Questions
1. Read the “Background” below. What types of bias do you think the networks display by almost no mention of a good possible solution to eradicating the Zika virus?
2. In September 2006 the World Health Organization announced:
Nearly thirty years after phasing out the widespread use of indoor spraying with DDT and other insecticides to control malaria, the World Health Organization (WHO) today announced that this intervention will once again play a major role in its efforts to fight the disease and said, “DDT presents no health risk when used properly.”
Why do you think there has been virtually no mention of the hope DDT could bring to the fight against the Zika virus (and of the WHO’s promotion of the use of DDT)?
3. Ask a parent or grandparent:
a) What do you know about DDT?
b) Please read the World Health Organization page on DDT, as well as the “Background” below. Does the WHO’s change of position on DDT change your view of the use of this insecticide? Explain your answer.
Scroll down to the bottom of the page for the answers.
Background
From Facts versus fears: DDT –
- The ban on DDT was considered the first major victory for the environmentalist movement in the U.S.
- The effect of the ban in other nations was less salutary, however.
- In Ceylon (now Sri Lanka) DDT spraying had reduced malaria cases from 2.8 million in 1948 to 17 in 1963. After spraying was stopped in 1964, malaria cases began to rise again and reached 2.5 million in 1969.
- The same pattern was repeated in many other tropical — and usually impoverished — regions of the world.
- In Zanzibar the prevalence of malaria among the populace dropped from 70 percent in 1958 to 5 percent in 1964. By 1984 it was back up to between 50 and 60 percent. The chief malaria expert for the U.S. Agency for International Development said that malaria would have been 98 percent eradicated had DDT continued to be used.
- In addition, from 1960 to 1974 WHO screened about 2,000 compounds for use as antimalarial insecticides. Only 30 were judged promising enough to warrant field trials. WHO found that none of those compounds had the persistence of DDT or was as safe as DDT. (Insecticides such as malathion and carbaryl, which are much more toxic than DDT, were used instead.) And – a very important factor for malaria control in less developed countries – all of the substitutes were considerably more expensive than DDT.
- And what of the charges leveled against DDT? A 1978 National Cancer Institute report concluded—after two years of testing on several different strains of cancer-prone mice and rats—that DDT was not carcinogenic. …
(Extract from the American Council on Science and Health publication “Facts Versus Fears” – Edition 3, June 1998.)
Answers
1. Bias by omission, story selection (no mention of the important news that the World Health Organization changed its position on DDT: very important for viewers to hear)
2. Opinion question. Answers vary.
3. Answers vary.