redo Jump to...
print Print...

- On September 15, Liberian Thomas Eric Duncan helped a neighbor’s family carry her into a taxi to bring her to a hospital maternity ward, where she was turned away. The 19-year-old woman returned to her house, where she died hours later from the Ebola virus.
- On September 19, when Duncan arrived at the airport in Monrovia, Liberia, his temperature was taken and recorded on a passenger screening form. It was 97.3 degrees Fahrenheit.
- The form asks travelers if they have any of 10 listed symptoms – among them, fever, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach pain and fatigue. Duncan answered “no” to all.
- He also was asked if he’d taken care of an Ebola patient or touched the body of anyone who’d died in an Ebola-stricken area in the last 21 days – the incubation period. He answered “no” to both questions as well.
(by Jake Miller, CBS News) – Despite concern about a domestic Ebola outbreak after the first diagnosis of the virus in the United States this week, senior officials with President Obama’s administration on Friday brushed aside a proposed ban on air travel to and from West African countries affected by the virus, arguing the move would be counterproductive.
Lisa Monaco, a homeland security adviser to the president, said during a news conference Friday at the White House that such a step could actually “impede” the response to the epidemic that has claimed over 3,400 lives to date.
The move would “slow down the ability of the United States and other international partners to actually get expertise and capabilities and equipment into the affected areas,” she said, suggesting that the best way to ultimately end the epidemic is to target it at its source in West Africa.
“The most effective way to go about controlling this is to prevent those individuals from getting on a plane in the first place,” she said. She noted that, since the beginning of the epidemic in March, “Dozens and dozens of people have been stopped from getting on flights in the region.”
She also said the U.S. has taken a number of steps to help Customs and Border Patrol personnel identify symptomatic individuals and prevent their entry, and she said the government is “constantly going to evaluate” best practices as containment efforts continue.
The first diagnosis of Ebola in the U.S. occurred on Monday, Sept. 29 in Texas. Thomas Eric Duncan, a Liberian national, left the West African nation on a flight bound for the U.S. on September 19. He was admitted on September 26 to Texas Health Presbyterian hospital in Dallas, complaining of flu-like symptoms, but he was released shortly thereafter. Two days later, when he returned to the hospital after his symptoms persisted, he was diagnosed with Ebola and placed in isolation.
Since then, officials have identified dozens of people who may have been exposed to the virus, and they’ve been working to contain any potential spread.
To prevent any more people stricken with Ebola from reaching the U.S., some politicians have called for a travel ban to and from the countries that have been hardest-hit by the epidemic.
“We should stop accepting flights from countries that are Ebola stricken,” said Gov. Bobby Jindal, R-Louisiana, in a statement. “Even countries in Africa have cut back on or stopped accepting flights from countries with Ebola outbreaks.”
The administration has said such a travel ban would be counterproductive, Jindal noted, but he added, “That statement defies logic. How exactly would stopping the entry of people potentially carrying the Ebola virus be counterproductive? This seems to be an obvious step to protect public health in the United States.”
And while he did not call for a travel ban, Sen. Richard Burr, R-North Carolina, slammed the administration for a response that has “been anything but fast and successful.”
“For the most prepared country in the world we are finding out just how ill-prepared we really are,” he said. “It is time to admit the realities that the current strategy to combat Ebola is not working. We need a designated leader, backed by the president, who can meet the urgency of this crisis head on and protect the American people, and end the confusion about who is charge of our total response effort.”
On Friday, Monaco was joined in the White House briefing room by several other senior officials, who all stressed that, despite any breakdowns in the system that occurred in Texas, the government has the situation well in hand.
“There were things that did not go the way they should have in Dallas,” acknowledged Dr. Anthony Fauci, the head of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, “but there were a lot of things that went right…the fundamental core basis of preventing an outbreak – contact tracing – is now going on.”
Fauci said it’s “entirely conceivable” there may be more cases in the United States, but he stressed that the United States has a robust health care infrastructure capable of preventing the kind of widespread outbreak that’s being seen in Africa.
“I take nothing lightly, but I’m convinced by what we have all said today that the system that’s in place…would make it extraordinarily unlikely that we would have an outbreak,” he said.
Monaco stressed that since the outbreak began in March, “tens of thousands” of individuals from affected countries have traveled to the U.S., and only one “isolated case in Texas” has resulted.
Health and Human Services Secretary Sylvia Mathews Burwell added, “We recognize the concern that even a single case of Ebola creates on our shores, but we have the public health systems and the public health providers in place to contain the spread of this disease.” …..
“The United States is prepared to deal with this crisis both at home and in the region,” Monaco said at the top of the briefing, neatly summarizing the administration’s attempts to reassure. “Every Ebola outbreak over the past 40 years has been stopped. We know how to do this, and we will do it again.”
Reprinted here for educational purposes only. May not be reproduced on other websites without permission from CBSNews. Visit the website at cbsnews .com.
Questions
1. a) Who is Lisa Monaco?
b) How did Ms. Monaco respond to the idea of banning air travel to and from West African countries affected by the Ebola virus? Be specific.
2. a) What does Ms. Monaco believe is the most effective way to control the spread of Ebola to the U.S.?
b) What steps does Ms. Monaco say have been taken to prevent Ebola victims from coming to the U.S.?
3. a) What steps has Louisiana Gov. Bobby Jindal said the U.S. should take to prevent Ebola victims from entering the U.S.?
b) How does Gov. Jindal respond to the Obama administration’s assertion that banning flights from West Africa would be counterproductive?
4. a) How does Dr. Anthony Fauci view the possibility of a widespread outbreak of Ebola in the U.S.?
b) What assurance did Secretary of Health and Human Services Sylvia Burwell give about Ebola in the U.S.?
c) Previous to Thomas Duncan’s diagnosis in Texas, U.S. government health officials had said it was unlikely that there would ever be a case of Ebola in the U.S.
Do Dr. Fauci’s and Secretary Burwell’s recent statements reassure you that we do not have to be concerned about an outbreak of Ebola in the U.S.? Explain your answer.
5. When a person is infected with the Ebola virus, it takes up to 21 days for the symptoms to appear.
a) Do you think the Obama administration’s plan for preventing people infected with Ebola from coming to the U.S. will be effective? Explain your answer.
b) Liberian citizen Thomas Duncan lied when asked if he’d taken care of an Ebola patient or touched the body of anyone who’d died in an Ebola-stricken area in the last 21 days. Do you think the Obama administration can prevent people from lying when questioned about whether they’ve come into contact with anyone stricken with Ebola? Explain your answer.
c) Ask a parent the same questions.
6. Ms. Monaco says stopping flights into and out of West Africa would “slow down the ability of the United States and other international partners to actually get expertise and capabilities and equipment into the affected areas.” How could the Obama administration impose a ban on flights to/from West Africa, yet still get our experts and equipment into the affected areas?
Background
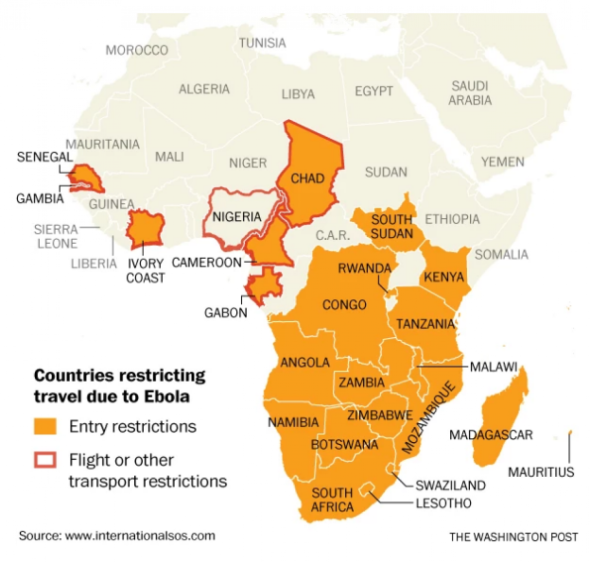
According to the Washington Post, several African nations have restricted or banned air travel from Ebola-stricken countries, and airlines including Kenya Airways, British Airways, Air Cote D’Ivoire and Nigeria’s Arik Air have suspended flights from the countries.
London’s Daily Mail reported: Air France has suspended flights to Sierra Leone because of the Ebola outbreak there and at the request of the French government. The decision comes a week after the airline’s staff signed a petition calling on their employer to avoid Ebola-hit countries for their own safety.
The map below is from the Washington Post article:
Daily “Answers” emails are provided for Daily News Articles, Tuesday’s World Events and Friday’s News Quiz.